Introduction
Cancer is a leading cause of death in pets, with millions of animals diagnosed annually. However, recent advancements in veterinary medicine are offering new hope. Cutting-edge research and technological innovations are revolutionizing pet cancer therapeutics, improving diagnosis, treatment, and overall outcomes for our beloved companions.
Definition
Treatments and drugs intended to identify, control, and possibly even cure cancer in animals are referred to as pet cancer treatments. Chemotherapy, surgery, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies specific to pet cancer kinds are some of these treatments. The objective is to decrease pain and suffering brought on by cancer in dogs, cats, and other companion animals while also enhancing quality of life and extending survival.
Immunotherapy: Harnessing the Body’s Natural Defenses
One of the most significant advancements in pet cancer therapeutics is the development of immunotherapy. This treatment modality leverages the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Immunotherapy has shown remarkable success in human medicine and is now being adapted for veterinary use.
Canine Melanoma Vaccine: One of the pioneering immunotherapies for pets is the canine melanoma vaccine, which is designed to treat dogs with malignant melanoma, a type of skin cancer. The vaccine stimulates the dog’s immune system to target and destroy melanoma cells, prolonging survival and improving quality of life.
Monoclonal Antibodies: Another promising immunotherapy involves the use of monoclonal antibodies. These lab-engineered molecules can specifically target cancer cells without harming healthy tissues. Monoclonal antibodies are being developed to treat various cancers in pets, including lymphoma and osteosarcoma.
Targeted Therapy: Precision Medicine for Pets
Targeted therapy is another breakthrough in pet cancer therapeutics, focusing on specific molecular targets associated with cancer. This approach allows for more precise and effective treatments with fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs): TKIs are a class of medications used in targeted therapy that block enzymes necessary for the development of cancer cells. Drugs like toceranib (Palladia) and masitinib (Kinavet) have been approved for treating mast cell tumors in dogs, offering a less toxic alternative to conventional chemotherapy.
Personalized Medicine: Advances in genomic sequencing have enabled personalized medicine approaches for pets. By analyzing the genetic profile of a pet’s tumor, veterinarians can identify specific mutations and tailor treatment plans to target those mutations, improving treatment efficacy.
Advancements in Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a cornerstone of cancer treatment, and recent technological advancements are enhancing its effectiveness for pets. Modern radiation therapy techniques are more precise, minimizing damage to healthy tissues and reducing side effects.
Stereotactic Radiation Therapy (SRT): SRT is a cutting-edge technique that delivers high doses of radiation to tumors with pinpoint accuracy. This approach is particularly beneficial for treating tumors in hard-to-reach areas or those that are resistant to conventional treatments.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): IMRT is another advanced radiation therapy technique that allows for more precise targeting of tumors. By modulating the intensity of the radiation beams, IMRT can deliver higher doses to the tumor while sparing surrounding healthy tissues.
Chemotherapy: New Formulations and Delivery Methods
While chemotherapy has been a mainstay of cancer treatment for decades, new formulations and delivery methods are making it more effective and less toxic for pets.
Metronomic Chemotherapy: This approach involves administering low doses of chemotherapy drugs continuously, rather than in high doses at intervals. Metronomic chemotherapy has been shown to inhibit tumor growth and spread while minimizing side effects.
Liposomal Formulations: Liposomal formulations of chemotherapy drugs encapsulate the active ingredients in lipid-based nanoparticles. This delivery method enhances drug accumulation in tumors, reducing toxicity and improving therapeutic outcomes.
Emerging Therapies: On the Horizon
In addition to the established therapies mentioned above, several emerging treatments are showing promise in pet cancer therapeutics.
Oncolytic Virotherapy: Oncolytic virotherapy involves using genetically engineered viruses to selectively infect and destroy cancer cells. Early studies in veterinary medicine have shown potential for treating various types of cancer, including lymphoma and osteosarcoma.
Gene Therapy: Gene therapy is an emerging field that aims to treat cancer by modifying the genetic material within cancer cells. Techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 are being explored for their potential to target and eliminate cancer cells with high precision.
Holistic and Integrative Approaches
Beyond conventional treatments, holistic and integrative approaches are gaining popularity in pet cancer care. These approaches combine traditional therapies with complementary treatments to support overall health and well-being.
Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting pets undergoing cancer treatment. Diets rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and high-quality proteins can help boost the immune system and improve the pet’s response to treatment.
Complementary Therapies: Therapies such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, and physical rehabilitation can help manage pain, reduce stress, and improve the quality of life for pets with cancer. To provide all-encompassing care, these therapies are frequently combined with traditional treatments.
The Role of Early Detection and Screening
Early detection is critical in improving the prognosis for pets with cancer. Advances in diagnostic tools and screening methods are enabling earlier and more accurate detection of cancer in pets.
Liquid Biopsy: Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive diagnostic test that analyzes blood samples for cancer-related biomarkers. This technique is becoming increasingly popular for early cancer detection and monitoring treatment response in pets.
Advanced Imaging: Imaging techniques such as MRI, CT scans, and PET scans are becoming more accessible in veterinary medicine. These advanced imaging modalities provide detailed insights into tumor size, location, and progression, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
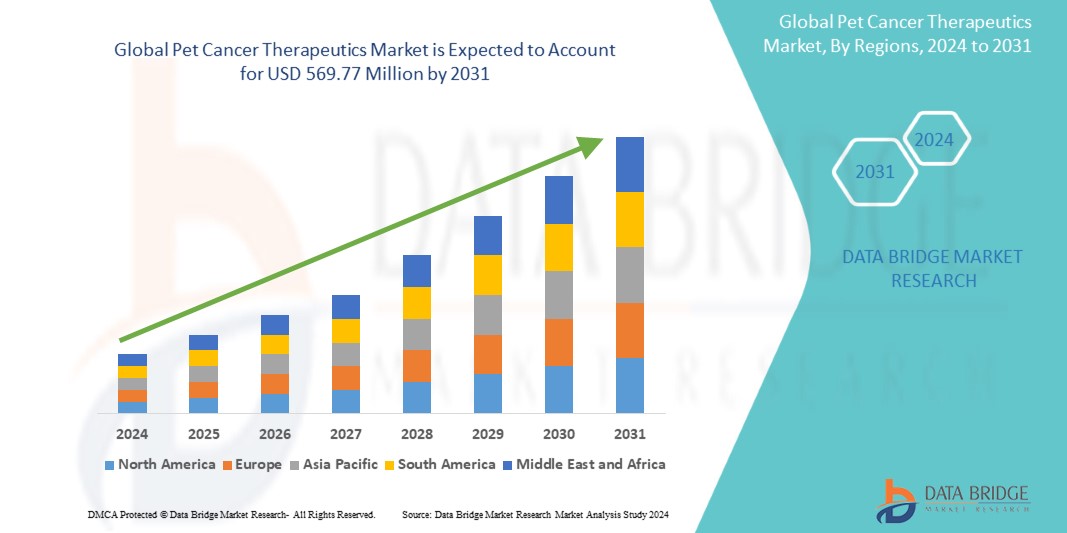
Growth Rate of Pet Cancer Therapeutics Market
The size of the global market for pet cancer Therapeutics was estimated at USD 283.86 million in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.10% to reach USD 569.77 million by 2031.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-pet-cancer-therapeutics-market
Conclusion
The landscape of pet cancer therapeutics is rapidly evolving, offering new hope for pets diagnosed with cancer. Breakthroughs in immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are transforming the way we treat cancer in pets, improving survival rates and quality of life. Emerging therapies and holistic approaches further expand the options available to pet owners, ensuring that pets receive the best possible care. As research and technology continue to advance, the future looks promising for pets battling cancer, providing them with a better chance at a longer, healthier life.



